
Climate adaptation means taking action to prepare for and adjust to both the current effects of climate change as well as the future impacts. The adjustments can be ecological, social, or economic, and respond to actual or expected climatic stimuli.
Examples of climate adaptation are:
- Building protective infrastructures such as building sea walls, elevating infrastructure, or retreating from low-lying coastal areas altogether;
- Preparing disaster and public health plans, in order to cope with climate emergencies;
- Farming more resilient type of crops in order to protect the food supply from climate impacts.
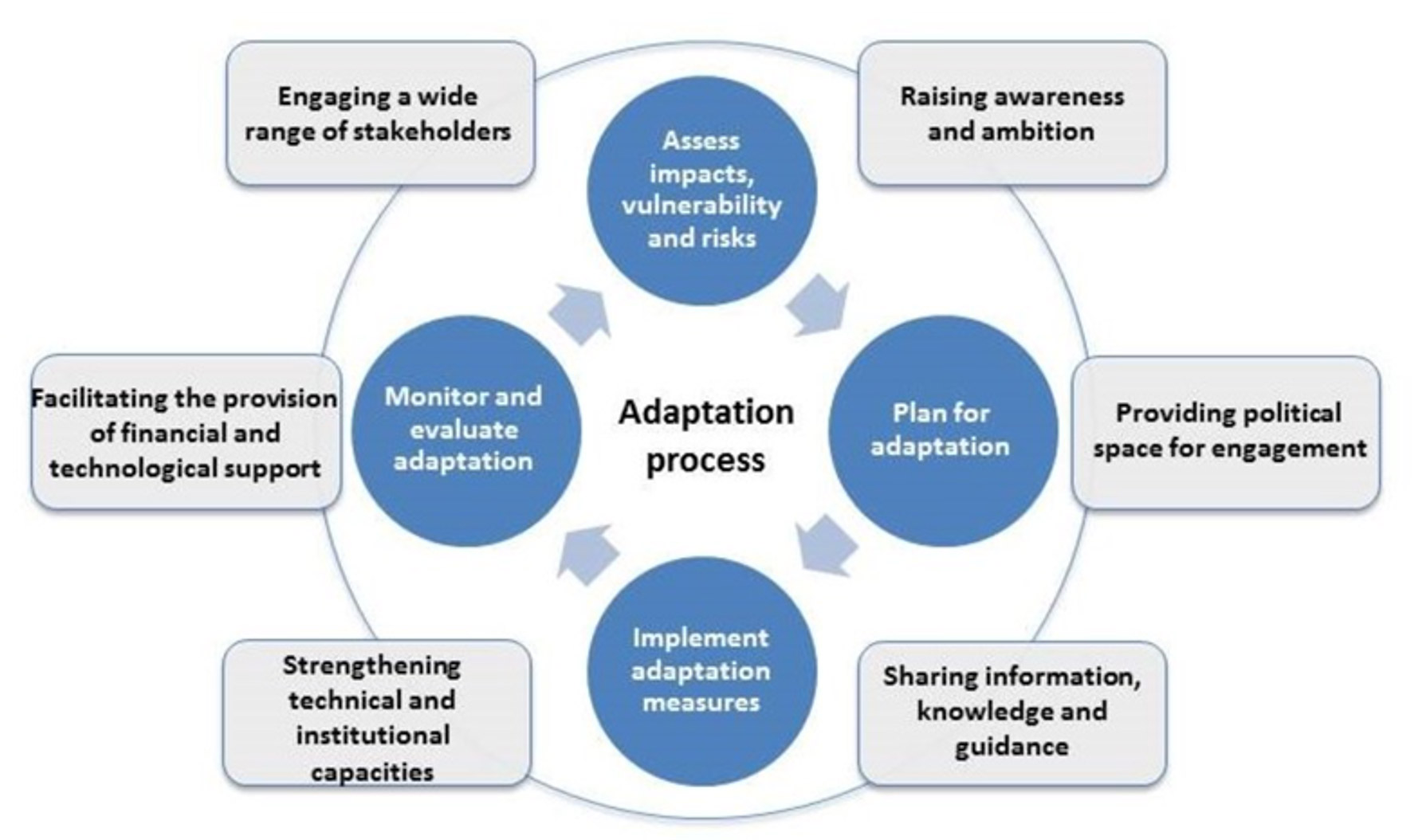
Climate mitigation means reducing or preventing emissions of greenhouse gases in order to prevent future climate impacts. Since Climate Change is mostly caused by the greenhouse gases that are released when burning coal, oil, and gas, reducing emissions is an essential step in mitigating adverse climate effects.
Examples of climate mitigation are:
- Modernization of technology across industries to ensure energy efficiency;
- Employment of renewable energies, such as solar, wind, and geothermal;
- Changes in management practices and consumer behaviour.
In this context, PROTECT aims at levering innovation procurement to boost the performance of the climate services market and support urgent action for climate adaptation, mitigation and resilience. PROTECT will do so by empowering procurers and specifically public authorities to take action for climate adaptation and mitigation by sharing content and formats that are readily usable by non-specialists to promote the benefits of EO-based climate services and allow them to identify and express their needs that could be met by climate services.
More information on the topic is available at:
